티스토리 뷰
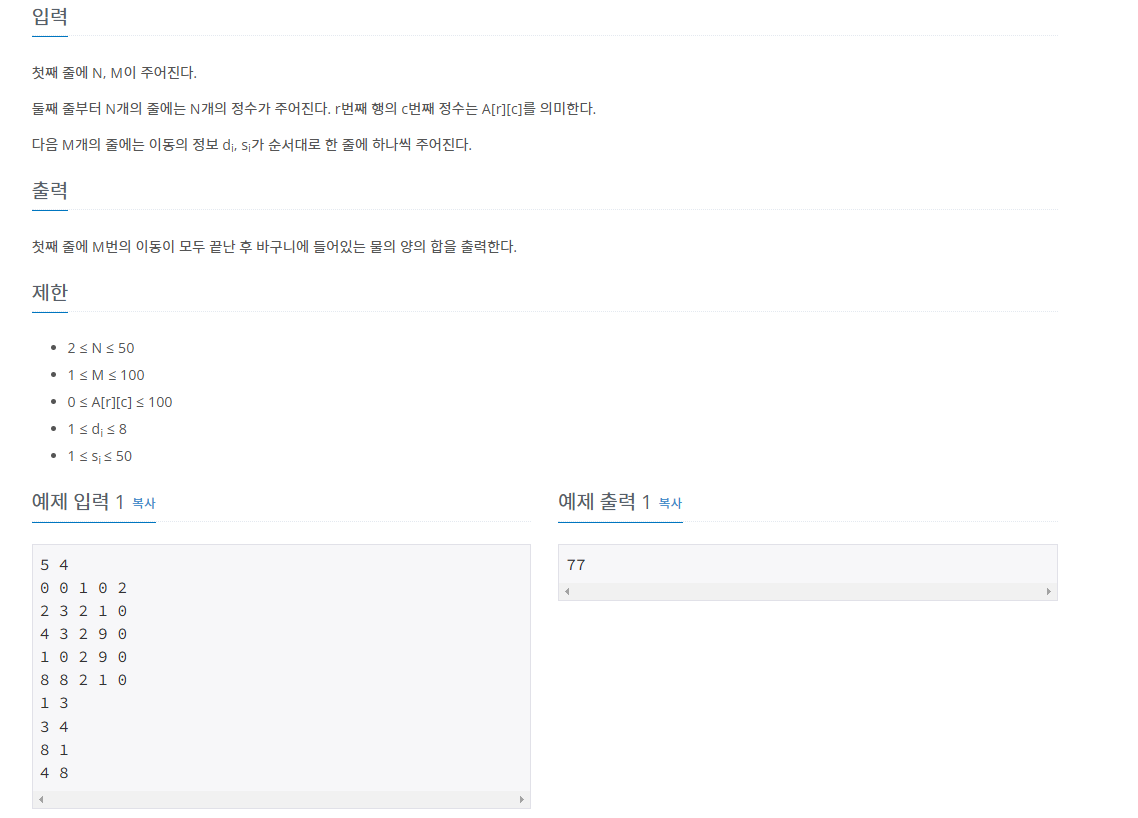
문제
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/21610



해결
시뮬레이션 문제 풀이 경험이 적던 필자는 "배열이 연결되어있다" 를 구현하기까지 많은 고민을 했었다. 아마 글을 보고 있는 다른 개발자 분들도 이 부분 구현하는 데 시간을 적지않게 쏟았으리라 생각된다.
구현 방법은 modulo 연산을 활용하는 것이다. 이 후 나머지 조건들을 충족시켜주면 된다. 자, 이제 코드를 보겠다.
1. modulo 연산을 활용하여 구름의 위치를 이동한다.
2. 물을 증가 시킨다.
3. 구름을 사라지게 한다. (newCloud로 대체)
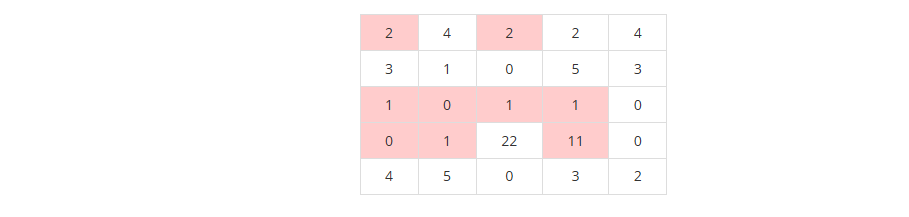
4. 물 복사 버그를 구현한다.
5. 새로운 구름을 생성한다.
- 기존 구름자리가 아니어야 함(!visited)
- 새로운 구름 영역의 물을 -2 시켜준다
package com.algorithm.boj.gold;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
public class 마법사상어와비바라기 {
static int N, M, totalWater;
static int[][] arr;
static boolean[][] cloud, visited;
static StringTokenizer st;
static int[][] dis = {
{0, -1},
{-1, -1},
{-1, 0},
{-1, 1},
{0, 1},
{1, 1},
{1, 0},
{1, -1}
};
public static void simulation(int d, int s) {
visited = new boolean[N][N];
boolean[][] newCloud = new boolean[N][N];
// 1. 구름 이동
for (int x = 0 ; x < N ; x ++) {
for (int y = 0 ; y < N; y ++){
if (cloud[x][y]){
// 모듈러 계산 (arr 확장 가능)
int nx = (x + dis[d][0]*s + N *100 ) % N;
int ny = (y + dis[d][1]*s + N *100 ) % N;
visited[nx][ny] = true;
newCloud[nx][ny] = true;
//2. 물 증가
arr[nx][ny] ++;
}
}
}
//3. 구름 사라진다
cloud = newCloud;
//4. 물복사 버그
for (int x = 0 ; x < N ; x++){
for (int y = 0 ; y < N ; y++){
if (cloud[x][y]){
int waterCount = 0;
for (int i = 1 ; i < 8 ; i+=2){
int nx = x + dis[i][0];
int ny = y + dis[i][1];
if (nx >= 0 && ny >= 0 && nx < N && ny < N && arr[nx][ny] > 0){
waterCount ++;
}
}
arr[x][y] += waterCount;
}
}
}
//5. 새로운 구름 생성 , -2 적용
newCloud = new boolean[N][N];
for (int x = 0; x < N ; x++){
for (int y = 0; y < N ; y++){
if (!visited[x][y] && arr[x][y] >=2){
newCloud[x][y] = true;
arr[x][y] -= 2;
}
}
}
cloud = newCloud;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
N = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
M = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
arr = new int[N][N];
cloud = new boolean[N][N];
// 초기 배열 입력
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
arr[i][j] = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
}
}
// 초기 구름 위치 설정
cloud[N-1][0] = true;
cloud[N-1][1] = true;
cloud[N-2][0] = true;
cloud[N-2][1] = true;
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++) {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
int d = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()) - 1;
int s = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
simulation(d, s);
}
totalWater = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
totalWater += arr[i][j];
}
}
System.out.println(totalWater);
}
}'알고리즘' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 백준 2667) 단지번호붙이기 java 자바 (2) | 2025.01.31 |
|---|---|
| 백준 2178) 미로탐색 자바 Java (1) | 2025.01.29 |
| java) 조합(combination) 문제 메모이제이션 기법 활용하기 (dfs) (2) | 2024.12.25 |
| java) 부분 집합 문제 DFS로 해결하기 (0) | 2024.12.22 |
| 백준 1753) 최단경로 Java 풀이 (0) | 2024.08.15 |
공지사항
최근에 올라온 글
최근에 달린 댓글
- Total
- Today
- Yesterday
TAG
- AWS
- 단지번호붙이기 자바
- dfs
- 백준 1965 풀이
- 백준
- 백준 그림 자바
- docker
- Java #객체 #자바기초 #자바
- StatefulSet
- 쿠버네티스 오브젝트
- 쿠버네티스 개념
- 프로그래머스
- ECR
- EB
- k8s
- 코딩테스트
- 단지번호붙이기 JAVA
- 행렬 테두리 회전하기 자바
- 자바
- 마법사 상어와 비바라기 자바
- EC2
- 구간합구하기
- java
- 백준 상자 넣기 자바
- 무중단배포
- 자료구조
- k8s object
- Java #코린이 #자바
- java #스프링 #spring #server
- 백준 상자넣기
| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
| 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 |
| 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 |
| 29 | 30 |
글 보관함
